- You are here:
- Home »
- Blog »
- ALS Care »
- Diet and Nutrition Guide for Individuals with ALS

Diet and Nutrition Guide for Individuals with ALS
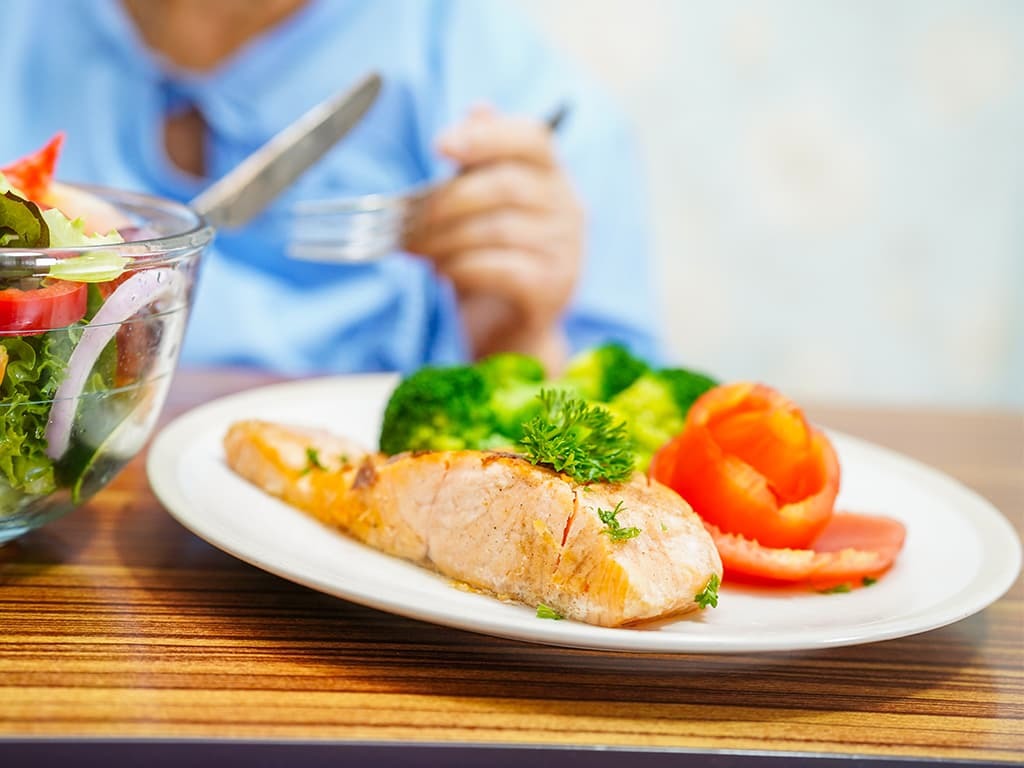
As with healthy individuals, diet and nutrition can play a significant role for those who have ALS. This chronic degenerative disease presents numerous challenges for the individuals who have it.
Difficulties with chewing and swallowing food become an increasing problem as ALS develops and making good dietary choices can make a huge difference, particularly in the early stages of the disease.
Poor nutrition can lead to greater fatigue, quicken the loss of muscle mass that occurs during the progression of ALS and lead to problems such as constipation and a reduced resistance to infection.
Here we take a closer look at the nutritional and dietary advice that individuals with ALS should consider. This is particularly important for those who may have had poor dietary habits prior to being diagnosed.
However, it’s essential that professional medical advice is sought before the individual makes any major changes in their diet, preferably from a doctor with experience in treating ALS patients.
Protein
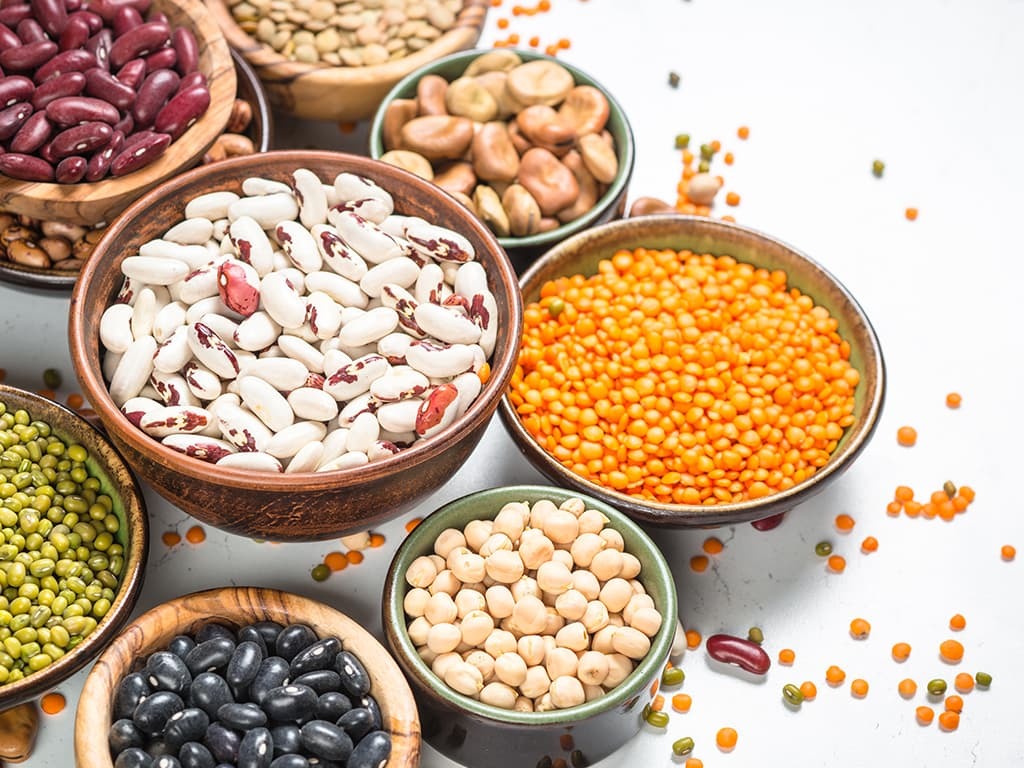

One of the key components of a healthy diet is protein. Take out the water from a human body and protein will make up 75% of its weight. Too much protein can be bad for the body, but too little can mean that it starts to break down muscle to feed its energy needs.
The good news is there are plenty of ways to get protein into the diet, even for someone who is vegan or vegetarian. All meats, poultry, fish, eggs and dairy contain high levels of it. It’s also found in legumes such as lentils, chickpeas and beans as well as soya and tofu.
One of the issues that individuals living with ALS have, especially as the disease progresses, is being able to chew and swallow. Adding sauce and mincing up protein can make it easier to consume.
Fiber
Fiber is also important in any diet and, without it, we can become clogged up and constipated. Dietary fiber comes in many form, including fruits and vegetables. For those who are unable to consume solids, options such as prune juice or fruit smoothies can help get the quantity required.
Fiber is not just good for regulating bowel movements, it also helps to maintain healthy blood pressure levels and reduce inflammation.
Calories
Individuals with ALS often struggle with maintaining body weight and eating enough. This can be down to lack of appetite but also because eating is actually difficult. Adding more fat into the diet can make a difference to the calorie count as can consuming smaller amounts regularly rather than eating one or two big meals at one time.
Water Intake
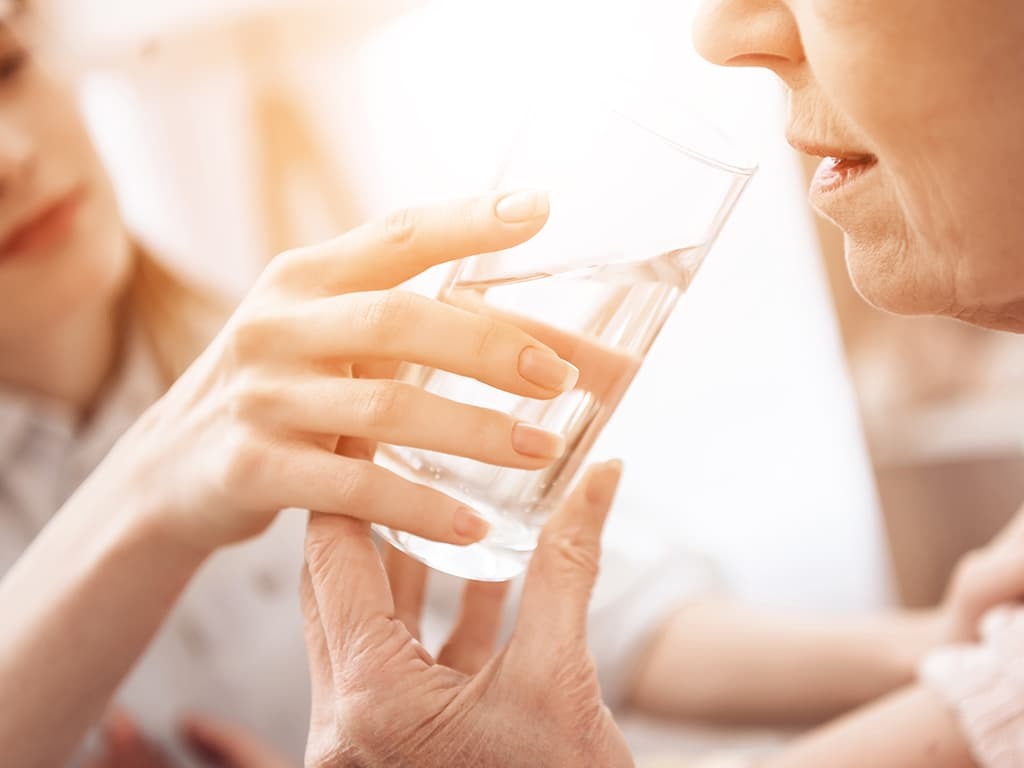

Keeping up fluid levels is also essential for those individuals who have ALS. If consuming water is difficult, swapping to thicker liquids such as smoothies and foods that have a high water content may be worth considering.
Dehydration can cause multiple problems including headaches, dry skin, dizziness and tiredness.
Ketogenic Diet and ALS
The ketogenic diet and ALS may seem like strange bedfellows but there is some sense to this. Our bodies are able to burn two fuels – carbohydrate and fat. The followers of the ketogenic diet believe that it’s much better to burn fat and there’s some evidence that this helps protect nerves. The diet basically switches your body from one method to another.
It’s worth noting that there has only been a small amount of research undertaken (on mice) regarding the ketogenic diet and neurodegenerative diseases and it’s not currently considered as a medical treatment for ALS.
However, ketogenic diets can also provide other benefits, such as boosting energy levels and maintaining a healthy weight.
The rules of the ketogenic diet state that the individual should eat 75% healthy fats, 20% protein and just 5% carbohydrate. In addition, carbohydrates should not include starchy or sugary fruits or vegetables. Instead, foods such as broccoli, avocado and nuts should be consumed.
Healthy fats include items such coconut oil, cheese, full-fat milk and fatty meats. While this goes contrary to a lot of nutritional advice that focuses on a high carb diet, there’s a growing body of evidence that fats are not as bad as we’ve been led to believe.
Feeding Tubes
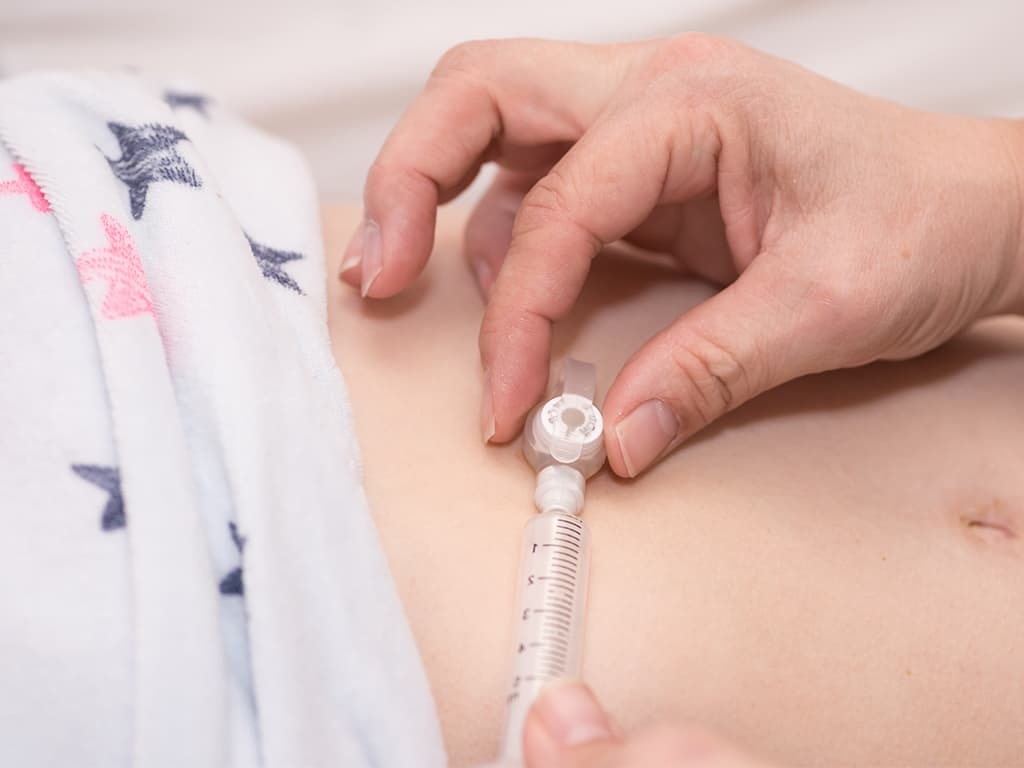
When eating and swallowing becomes too difficult for an individual with ALS, the solution is often to use a feeding tube. This helps reduce the risk of choking, while providing the opportunity to administer food and water as well as medication if needed.
The feeding tube is generally inserted directly into the stomach and liquid nutritional supplements are delivered using a syringe. For many people with ALS in the later stages of the disease, this removes the stress and anxiety of having to try and swallow food and can be something of a relief.
The Importance of Nutrition
Through all stages of ALS development, nutrition is vitally important.
Ensuring that the individual gets the right amount of nutrients, fiber, calories and water can make a huge difference to their sense of wellbeing and overall health.
